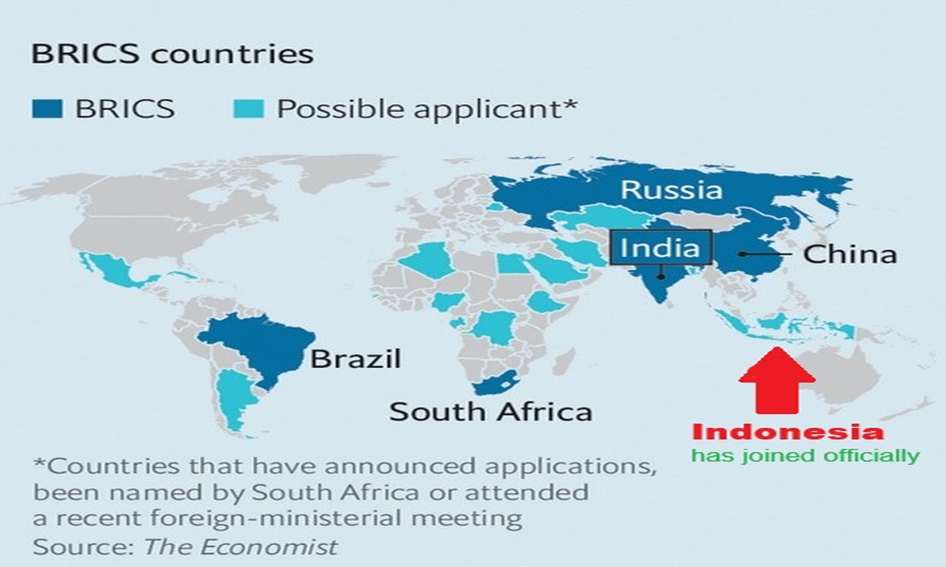
Context: Indonesia has officially become a full member of BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa). This decision was unanimously endorsed at the 2023 BRICS Summit in Johannesburg and was announced by Brazil, which holds the BRICS presidency in 2025.
What is BRICS?
- BRICS is a coalition of countries dedicated to promoting economic growth, development cooperation, and reforming global governance.
BRICS concentrates on collaboration in three main areas:
- Political and Security Cooperation: Working towards peace, global stability, and reforms in governance.
- Economic and Financial Cooperation: Encouraging trade, investment, and strengthening economic resilience.
- Cultural and People-to-People Cooperation: Fostering mutual understanding and social connections.
Present Members of BRICS
- Original Members: Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- Recent Additions: Indonesia, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the UAE.
| Evolution of BRICS: 2001: The term “BRIC” was introduced by Jim O’Neill, an economist at Goldman Sachs, in a report that identified Brazil, Russia, India, and China as rapidly growing economies. 2006: BRIC leaders held their inaugural meeting at the G8 Outreach Summit in St. Petersburg, Russia. 2009: The first BRIC Summit took place in Yekaterinburg, Russia, formalizing the grouping. 2010: South Africa became a member, transforming BRIC into BRICS. 2014 Fortaleza Declaration: The creation of the New Development Bank (NDB) and the Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) were major milestones in financial cooperation. Recent Expansion: In 2023, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, and the UAE joined, marking BRICS’ growing influence in the Global South. 2025: Indonesia officially became a member. |
Significance of BRICS:
- Economic Growth: Plays a key role in driving global economic expansion, accounting for 24% of global GDP and over 16% of global trade.
- Advocacy for a Multipolar World: Supports the idea of a multipolar global order, challenging Western dominance in international governance.
- South-South Cooperation: Enhances collaboration among developing nations to address common challenges such as poverty and climate change.
- Alternative Financial Systems: Investigates alternatives like the New Development Bank (NDB) and Contingent Reserve Arrangement (CRA) to reduce dependence on Western financial institutions and the US dollar.
Challenges Faced by BRICS:
- Diverging Interests: BRICS members have varying priorities, such as the tensions between India and China, along with differing views on global issues.
- Economic Disparities: There are significant differences in economic size and capacity among the members, with China accounting for a major share of BRICS’ GDP.
- Institutional Weakness: The lack of a formal structure and binding agreements reduces the bloc’s effectiveness.
- Geopolitical Pressures: External challenges, including Western sanctions on Russia and tensions between the US and China, put BRICS’ unity and neutrality to the test.

